Enhancing Sensory Processing with Sensory Integration Therapy
Sensory integration therapy is designed to help children who experience sensory processing challenges respond to sensory input more regulated and effectively. It can play a vital role in improving a child’s sensory awareness, emotional regulation, and overall well-being. At the core of this therapeutic approach is the Sensory Diet Toolkit, a collection of activities and interventions that support sensory processing and help children navigate their sensory needs throughout the day.
What is Sensory Integration Therapy?
Sensory integration therapy is a treatment approach that focuses on how the brain processes and responds to sensory information. It helps children become more aware of their sensory experiences, such as touch, sound, sight, and movement. The therapy aims to balance how a child responds to different sensory stimuli, helping them function better in everyday environments like home, school, and playgrounds.
For children with sensory processing disorders, such as those with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), ADHD, or other developmental conditions, sensory integration therapy can make a significant difference. It can improve how children respond to sensory experiences, whether feeling overwhelmed by loud noises or seeking out constant motion.
What is a Sensory Diet?
A sensory diet is a personalized set of sensory activities strategically scheduled throughout the day to help the child meet their sensory needs. It is called a “diet” because it involves a routine of activities providing specific sensory input to regulate the sensory system. Think of it as a balanced approach to sensory stimulation—just like a balanced meal plan supports your physical health, a sensory diet supports emotional and sensory well-being.
The Sensory Diet Toolkit: Key Components
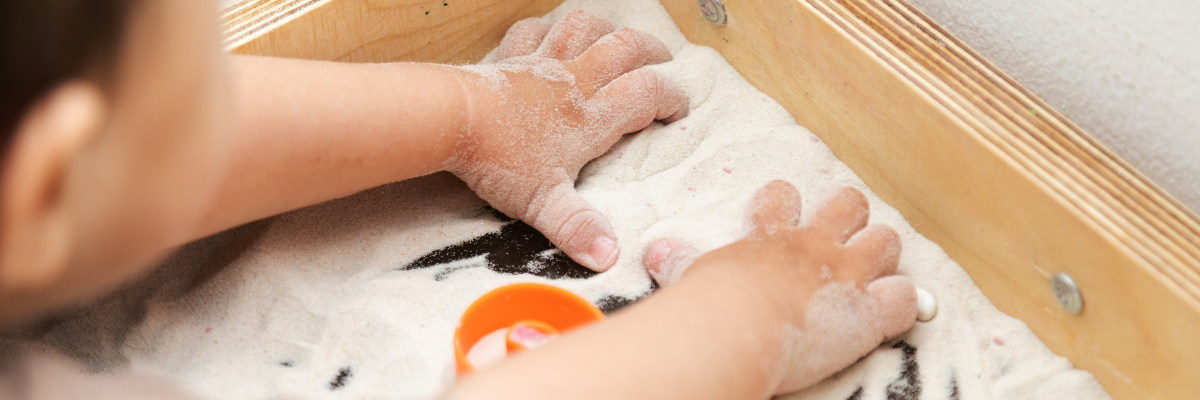
The Sensory Diet Toolkit consists of various activities as well as strategies to help children with sensory processing challenges. These activities stimulate, calm, or organize the sensory system, depending on the child’s specific needs. Here are some examples:
- Therapeutic Brushing: This involves using a special brush to apply gentle pressure to the skin, providing calming tactile input. It can help children who are sensitive to touch or who have difficulty calming down.
- Therapeutic Drumming: Using drums or rhythmic activities helps children who need proprioceptive input (sensory input related to body movement) to organize their movements and also improve focus.
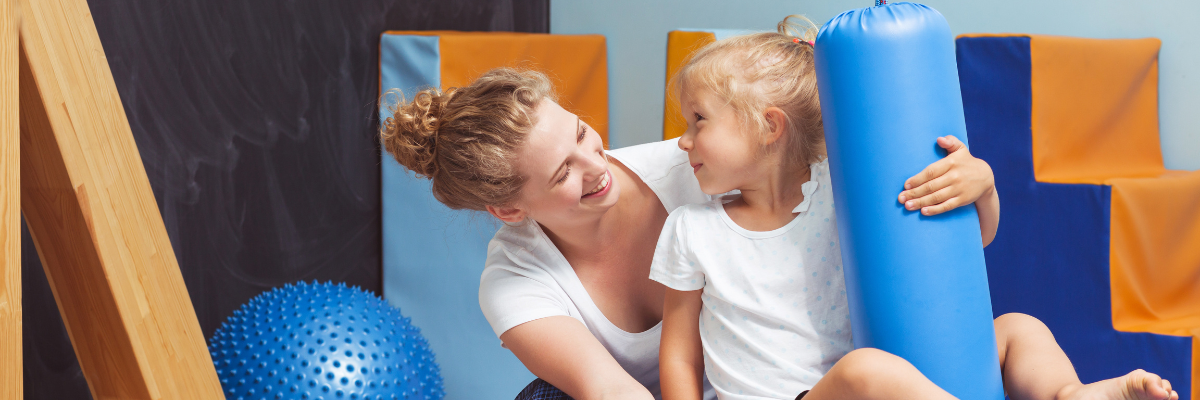
- Deep Pressure Techniques: Activities like squeezing a stress ball or using weighted blankets can help children who need calming sensory input to feel more grounded and relaxed.
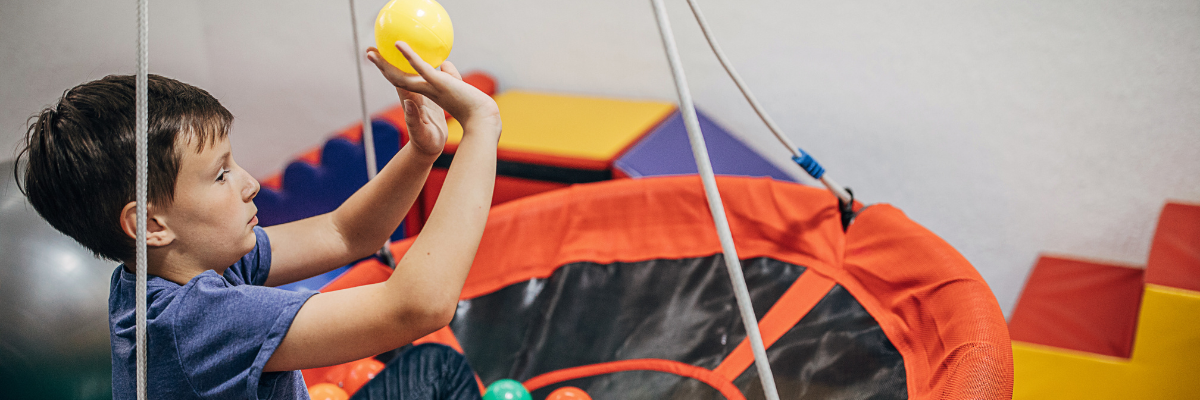
- Movement Breaks: Short bursts of physical activity like jumping on a trampoline or spinning can help children who seek sensory input and also may need extra stimulation to feel regulated.
- Fidget Tools: Fidget spinners, chewable jewelry, or putty provide sensory input that helps children stay calm and focused, especially in situations that may be overstimulating.
How the Sensory Diet Helps Children
By integrating sensory activities into daily routines, children can improve their ability to process sensory information, which can help them:
- Stay calm and focused: Sensory activities help children regulate their emotional as well as physical responses, promoting a more balanced state of being.
- Develop better social skills: By managing sensory needs, children may have fewer meltdowns or emotional outbursts, allowing them to interact more comfortably with others.
- Improve motor skills and coordination: Sensory activities also support the development of fine and gross motor skills, which can lead to improved physical coordination.
- Enhance emotional well-being: Children who can self-regulate their sensory input are better equipped to handle stress, frustration, and other emotional challenges.
How Carolina Therapy Connection Can Help
At Carolina Therapy Connection, we offer sensory integration therapy as part of our comprehensive therapy services for children. Our team of skilled occupational therapists assesses your child’s unique sensory processing needs and creates a personalized sensory diet that works for them. Whether your child struggles with sensory overload, seeks constant movement, or finds it difficult to focus, we can help with strategies tailored to their needs. If you want to learn more about sensory integration and how we incorporate this approach into therapy, including intensives, please schedule an evaluation. You can also use this link to explore more about our pediatric intensive therapy services.