Why Sleep Matters: Sleep Strategies Key to a Well-Rested Child
Parenting can be a rollercoaster ride filled with joy, challenges, and sleepless nights. Nights without sleep might seem normal in the newborn phase, but they don’t have to be a permanent part of parenting! Do you know some simple sleep strategies that can help the family sleep better? This blog post will explore tips to make bedtime a breeze for you and your kids!
The Power of Routine: Sticking to a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Consistency is key when it comes to sleep! Using a regular sleep schedule helps create a clock inside your child’s body. It also helps to create a predictable routine for your child. Try to get to bed and wake up simultaneously every day. That includes weekends! This will help the body create a regular sleep pattern and make falling asleep easier.
Create a Nightly Routine
Ensuring a good night’s sleep starts before your child’s head hits the pillow. Create a consistent bedtime routine. Before bed, try taking a warm, calming bath. Read a book in bed or try relaxation strategies like listening to calming music or stretching. Limit snacks, drinks, and screen time before bed.
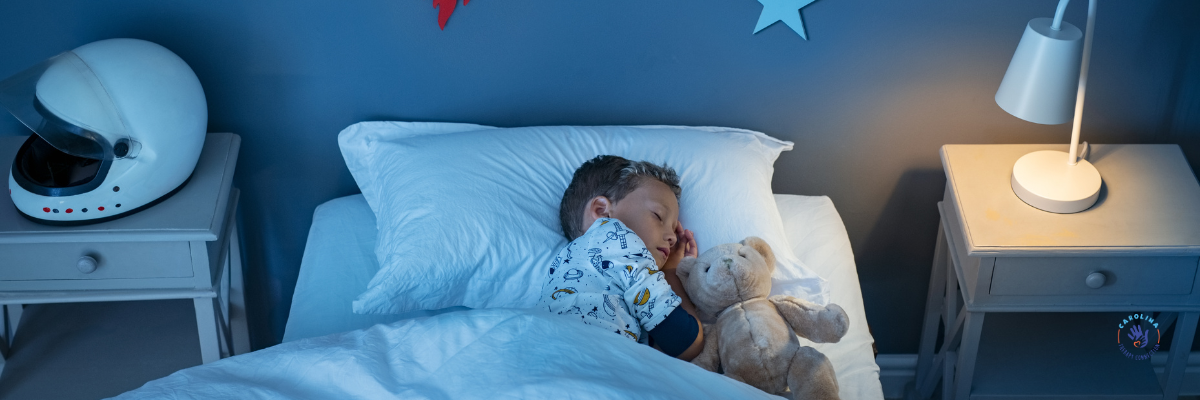
Creating a Sleep-Friendly Environment for Your Child
Turn your child’s bedroom into a space that encourages sleep. Keep the space quiet and dark. You can use blackout curtains to block light and a white noise machine to drown out any noise. Temperature is also critical. Make sure your child is not too hot or too cold. The actual place of sleep can make or break a good night of sleep. Ensure your child’s mattress and pillows provide good support for a restful sleep. You can also try stretchy lycra sheets to provide compression during sleep, making your child feel as if they are getting a comfy hug all night long. If your child displays fear of the dark, use a night light to provide a comforting light while sleeping.
The Role of Screen Time in Your Child’s Sleep Quality
The light from screens like phones, tablets, or TVs can interfere with sleep. Try to avoid using screens for at least an hour before bedtime. It may also be helpful to remove screens from the bedroom. Instead, read a book, draw, or play a quiet game to help when winding down before bed.
Daytime Activities That Promote Better Sleep at Night
Did you know that being active during the day can help you sleep better at night? Please encourage your child to get outside to play or do some fun movement activities to help their body feel tired when it’s time to lay their heads down.
Nutrition and Sleep: What to Eat and Avoid Before Bedtime
Some foods and drinks make it harder for your child to fall asleep. Avoid eating large meals or spicy foods before bed, as they can cause discomfort during sleep. Try not to have snacks or drinks with caffeine or sugar before bedtime. Instead, stick to a light, healthy snack that won’t disrupt their sleep.
Follow these simple tips to become a sleep superstar and have sweet dreams every night! Remember, getting enough sleep is essential for staying healthy, so prioritize a good night’s sleep.
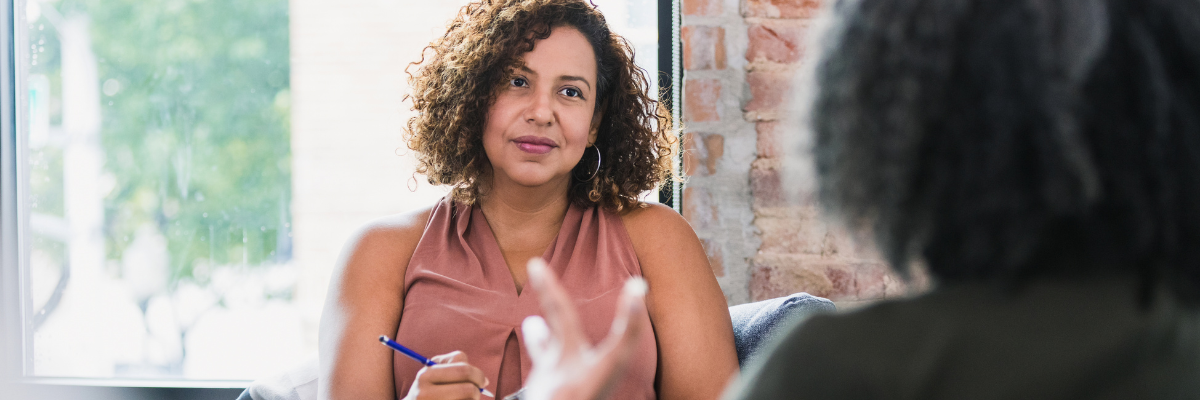
How Carolina Therapy Connection Can Support Better Sleep?
In addition to utilizing the tips above at home, we know that sometimes families may need extra support. At ***@***********************on.com","type":"person"}”>Carolina Therapy Connection, our Occupational Therapists work to address any barriers that affect someone’s physical, mental, or emotional well-being. Occupational therapists at CTC can help determine if your child’s sleep difficulties are related to underlying sensory or environmental issues. They can help establish a sensory diet (a personalized, organized plan that provides sensory input activities that a person needs to regulate their body throughout the day) to address potential underlying sensory issues that may impact sleep. They can also provide additional strategies for your child’s specific sleep needs. Our goals are to improve your child’s sleep quality to increase participation in meaningful activities throughout the day. Additionally, check out our Amazon storefront for items that can help achieve a good night’s sleep!
By: Caroline Zissette, MS, OTR/L